Learn All About Zinc
Zinc
Found in soil, air, and water.
Found in soil, air, and water.
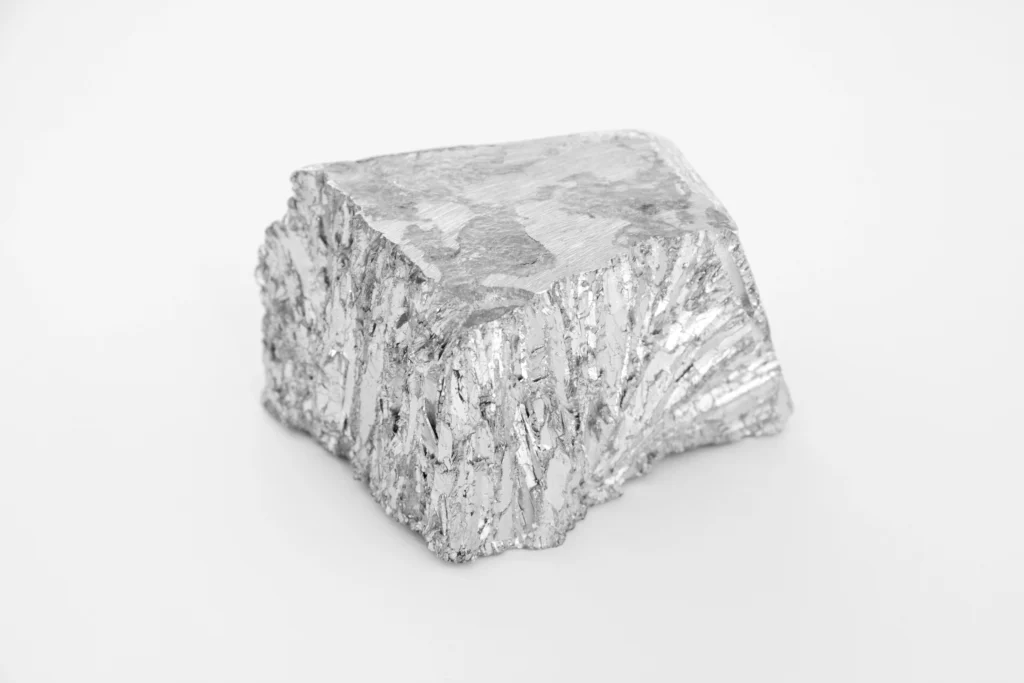

Zinc is a bluish-white, lustrous metal with the chemical symbol Zn. It is the 24th most abundant element in Earth’s crust and the 4th most widely consumed metal globally, behind iron, copper, and aluminum. It is found in soil, air, and water and is present in food. At room temperature, zinc is a slightly brittle metal, but it becomes malleable at 100° C (212° F). Above 210°C, it becomes brittle again and can be pulverized. Zinc and other base metals, such as copper and lead, are commonly found together in mineral deposits.
Zinc’s unique combination of physical and chemical properties makes it indispensable across various sectors, including construction, manufacturing, and electronics. Zinc is also essential for human health, playing a crucial role in immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis.
Zinc was used in Rome and China more than 2000 years ago as a component of brass. Commercial production of zinc did not start in Europe until the middle of the 18th century and in the United States until 1860.
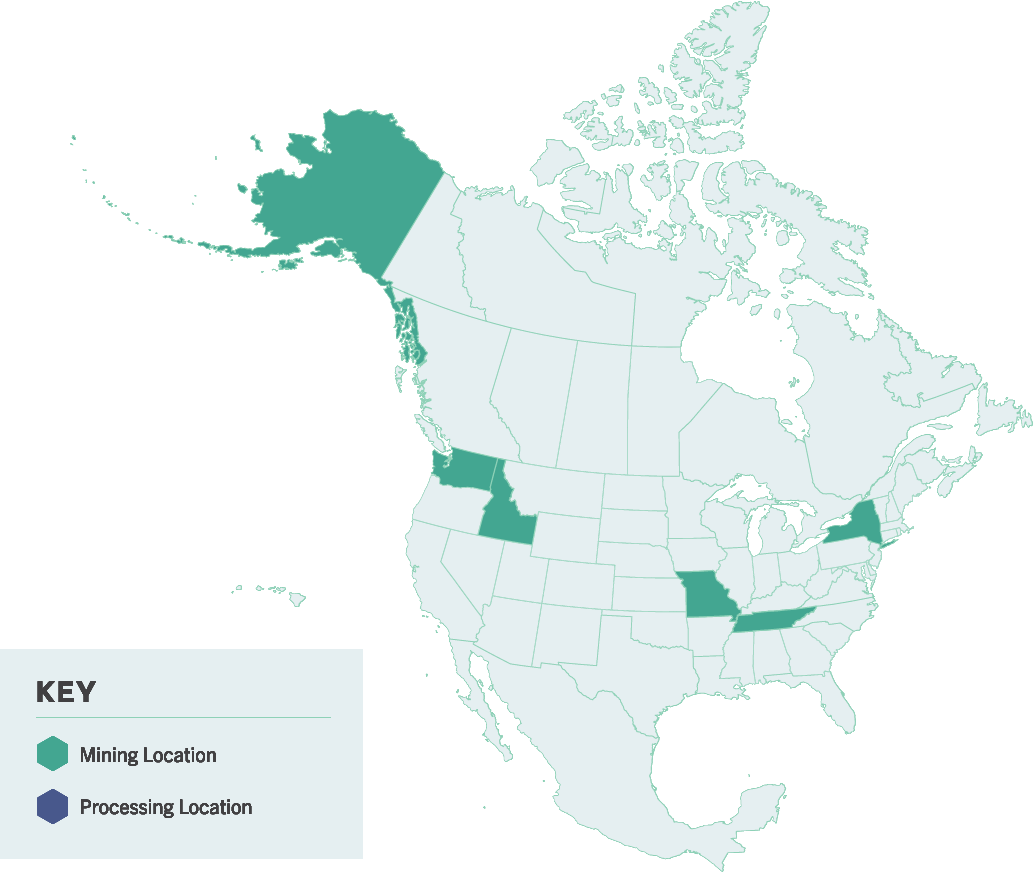
Wait there’s more! Click below to learn about the rest of our essential minerals.